Five Key Diagrams of Cat Anatomy Simplified
Did you know that understanding the key diagrams of cat anatomy can provide valuable insights into their physiology and behavior?
From their external features to intricate skeletal structures, each diagram unveils fascinating details about your feline friend.
By exploring these simplified diagrams, you will gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and elegance of a cat's anatomy.
External Features
When examining a cat's external features, start by observing its fur texture and color. The coat coloration of a cat can vary greatly, ranging from solid colors like black or white to intricate patterns like tabby stripes or calico patches. This aspect of a cat's appearance isn't only aesthetically pleasing but can also give you clues about its breed or genetics.
Moving on to ear shape, cats can have different ear shapes that are specific to certain breeds. Some cats have ears that are more rounded, while others have ears that are pointed. The shape and size of a cat's ears can also play a role in its hearing abilities, with larger ears often indicating a better sense of hearing.
As you continue to observe the external features of a cat, take note of any unique characteristics that make it stand out. Whether it's a rare coat coloration or distinctive ear shape, these features all contribute to the overall appearance and personality of the cat. By paying attention to these details, you can deepen your understanding and appreciation of the diversity within the feline world.
Skeletal Structure
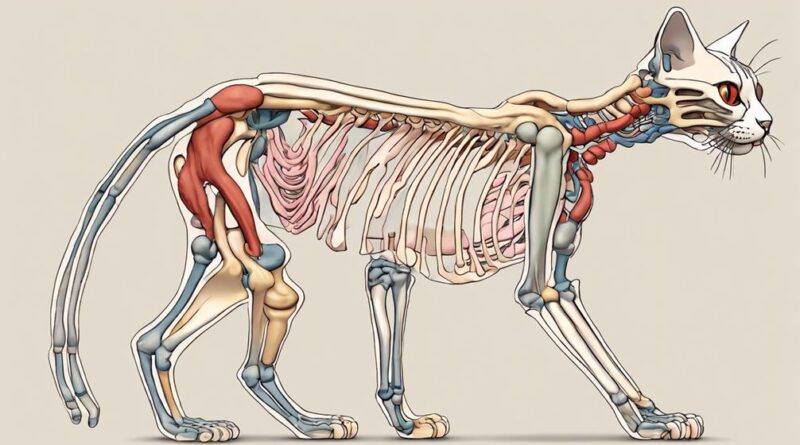
Explore the intricate skeletal structure of a cat to understand its anatomy better. The skeletal system of a cat provides the framework that supports its body and allows for feline movement. Cats have a highly flexible spine with around 30 vertebrae, giving them their characteristic agility and ability to land on their feet. This adaptability is due to the presence of additional vertebrae compared to humans, enabling them to twist and turn with ease.
The cat's skeleton includes long bones like the femur and humerus, which are crucial for strength and mobility. Their shoulder blades aren't attached to the rest of the skeleton, allowing for greater flexibility when climbing or jumping. The hind legs of a cat are powerful, with strong muscles attached to the femur, aiding in swift movements and impressive leaps.
The skull of a cat is uniquely designed to accommodate its sensory organs, such as large eye sockets for excellent vision in low light and sharp teeth for hunting. Understanding the skeletal structure of a cat provides insight into how these amazing creatures move with grace and precision. Next, we'll delve into the muscular system to see how muscles work in conjunction with the skeletal system to facilitate a cat's movements.
Muscular System
The muscles in a cat's body work intricately with the skeletal system to enable agile movements and graceful actions. Muscle function is crucial for a cat's ability to pounce, climb, and stretch effortlessly. Here are some key points to understand about a cat's muscular system:
- Diverse Muscle Types: Cats possess various types of muscles, including smooth muscles that control internal organs, cardiac muscles that keep the heart beating, and skeletal muscles that enable movement.
- Flexibility and Strength: The combination of flexibility and strength in a cat's muscles allows for swift and powerful movements, essential for hunting and play.
- Coordination for Balance: The muscles in a cat's body work in harmony to maintain balance, coordination, and stability, aiding them in activities like walking on narrow ledges with precision.
- Precision in Movements: Cats have finely tuned muscles that enable them to make precise movements, such as gracefully extending their claws or twitching their ears to listen intently.
- Efficient Energy Utilization: Through their muscular system, cats can conserve energy when needed, like when they crouch low before pouncing with explosive force, showcasing the efficiency of their muscles in cat movement.
Respiratory System
With a complex network of organs and muscles, a cat's respiratory system efficiently facilitates oxygen intake and carbon dioxide release. The process of gas exchange occurs in the lungs, where oxygen from the inhaled air enters the bloodstream, and carbon dioxide is removed from the blood to be exhaled. Cats have a unique breathing mechanics compared to humans, utilizing both their chest and diaphragm to expand and contract the lungs efficiently.
When a cat inhales, the chest cavity expands, allowing air to rush into the lungs. The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle located below the lungs, contracts and flattens, further aiding in the expansion of the chest cavity. This coordinated effort creates negative pressure within the lungs, drawing air in. On the exhale, the process reverses as the chest cavity contracts, and the diaphragm relaxes, pushing air out of the lungs.
Cats are obligate nose breathers, meaning they primarily breathe through their noses. This helps regulate airflow and ensures that the air they breathe is warm and moist before reaching the lungs. Understanding the intricate respiratory system of a cat is crucial for maintaining their overall health and well-being.
Digestive System
Efficiently processing nutrients from food, a cat's digestive system works diligently to break down and absorb essential elements for their overall health and energy. The digestive system of a feline plays a crucial role in extracting nutrients from food and eliminating waste efficiently.
Here are some key points to better understand the intricacies of a cat's digestive system and how it impacts their feline nutrition:
- Specialized Teeth: Cats have sharp, pointed teeth designed to help them grasp, shred, and chew their food effectively, aiding in the initial breakdown of food particles.
- Short Digestive Tract: With a relatively short digestive tract, cats are adapted for a diet rich in proteins and fats, enabling quick digestion and absorption of essential nutrients.
- High Protein Requirements: Due to their carnivorous nature, cats require a diet high in protein to meet their energy needs and maintain muscle mass.
- Sensitive Stomach: Cats can have sensitive stomachs, making it important to introduce new foods gradually to prevent digestive upset.
- Importance of Water: Feline nutrition isn't just about food; water is essential for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall hydration.
Understanding the unique features of a cat's digestive system is crucial for providing them with a balanced diet that meets their feline nutritional needs.
Circulatory System
To understand the circulatory system of a cat, consider how this intricate network of vessels and organs plays a vital role in delivering oxygen and nutrients throughout their body. The cardiovascular function in cats is essential for their survival, ensuring that every cell receives the necessary oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. Blood circulation in cats follows a similar pattern to humans, with the heart acting as the central pump that propels blood through arteries, capillaries, and veins.
In cats, the heart is a powerful organ responsible for circulating blood throughout the body. The blood carries oxygen and nutrients that are vital for the cat's overall health. As the heart beats, it pushes oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the rest of the body through arteries. These arteries branch out into smaller vessels called capillaries, where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged for waste products. The deoxygenated blood then returns to the heart through veins to be pumped to the lungs for reoxygenation.
Understanding the cat's circulatory system is crucial for recognizing signs of cardiovascular issues that may affect your feline friend's health. By ensuring a healthy circulatory system through proper nutrition and regular exercise, you can help your cat lead a long and healthy life.
Nervous System
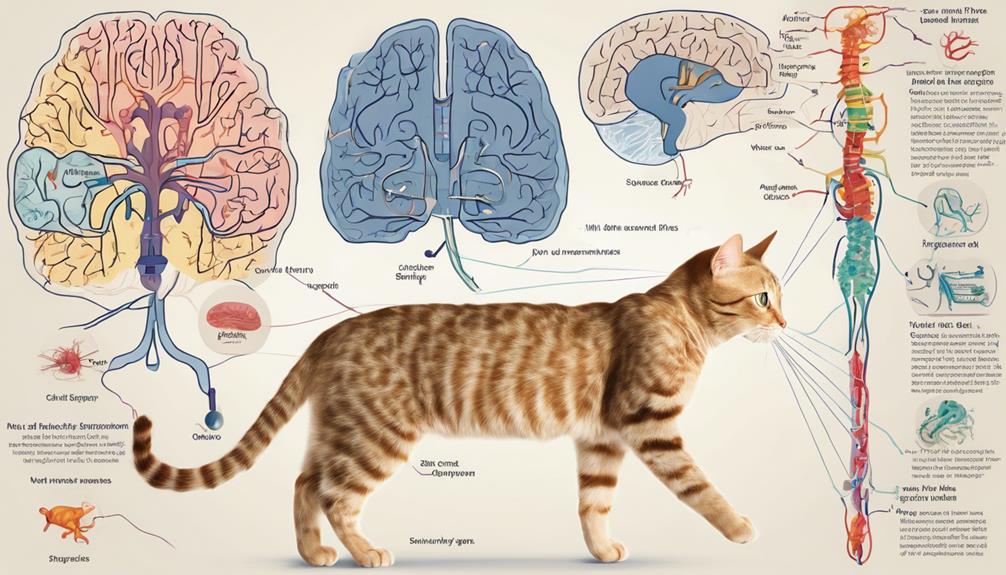
The intricate web of neurons in a cat's body orchestrates its every movement and sensation, showcasing the complexity of the feline nervous system. This intricate system is responsible for coordinating various functions within the cat's body, from basic reflexes to complex behaviors.
Here are some key points to help you understand the feline nervous system better:
- Brain Function:
The brain of a cat plays a crucial role in processing information received from the senses, controlling movements, and regulating essential bodily functions. It's where thoughts, emotions, and memories are formed.
- Spinal Cord Function:
The spinal cord serves as the main pathway for transmitting information between the brain and the rest of the body. It plays a vital role in reflex actions and motor coordination.
- Sensory Perception:
Cats have highly developed senses, including sharp vision, acute hearing, and a strong sense of smell. The nervous system processes these sensory inputs, allowing cats to navigate their environment effectively.
- Motor Control:
The nervous system coordinates muscle movements, allowing cats to walk, run, jump, and engage in various other activities with precision and agility.
- Autonomic Functions:
The feline nervous system also regulates automatic bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiration, ensuring the cat's overall well-being.
Reproductive System
With intricate biological mechanisms at play, the cat's reproductive system functions as a vital component of its overall physiology. The reproductive system of a cat is intricately designed for mating behavior and ensuring the continuation of the species. Male cats have testes that produce sperm, while female cats have ovaries that release eggs.
During mating behavior, male cats exhibit certain characteristics like spraying urine to mark territory and vocalizing loudly to attract females. Female cats, on the other hand, may display behaviors such as yowling and restlessness when in heat to signal their readiness to mate.
When a female cat mates, the male's sperm fertilizes her eggs, leading to pregnancy. The gestation period for cats is around 63-65 days, after which the female gives birth to a litter of kittens.
Understanding the cat's reproductive system is crucial for responsible pet ownership. It allows pet owners to make informed decisions about spaying and neutering to control the cat population responsibly. By being knowledgeable about the reproductive system, cat owners can contribute to the welfare of both their pets and the feline community as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Cats' Whiskers Help Them Navigate Their Surroundings?
Your cat's whiskers aren't just cute accessories; they play a crucial role in helping them navigate their surroundings.
Whisker sensitivity enables cats to sense changes in the environment by detecting even subtle air movements. This sensory adaptation allows them to gauge distances, navigate in low light, and avoid potential obstacles.
Therefore, your feline friend's whiskers are like a built-in GPS system that helps them move around confidently and safely.
What Is the Purpose of a Cat's Dewclaw?
The dewclaw function in feline anatomy is to provide extra gripping power. This small claw-like digit located higher up on the cat's leg than the other claws helps cats with balance and stability while climbing or running.
It also aids in grooming by giving them more precision. Dewclaws are like an extra thumb, assisting your feline friend in various activities and movements.
Why Do Cats Have a Third Eyelid, or Nictitating Membrane?
Cats have a third eyelid, or nictitating membrane, for protection and moisture. This thin, translucent membrane sweeps across the eye to keep it moist, shielded from debris, and helps with tear spreading.
The third eyelid function is vital for maintaining eye health and ensuring clear vision. It's a natural defense mechanism that adds an extra layer of protection to your cat's eyes, keeping them healthy and functioning properly.
How Do Cats' Retractable Claws Work?
When your cat retracts its claws, the claw mechanics involve the intricate paw anatomy and nail retraction process. The functionality of their retractable claws allows them to stay sharp and protected when not in use.
This unique feature benefits cats by enabling them to hunt effectively and climb with precision. Understanding how their claws work can help you appreciate the design and capabilities of your feline friend.
What Is the Purpose of a Cat's Grooming Behavior?
When it comes to a cat's grooming behavior, it serves multiple purposes. Not only does it keep their fur clean and free of parasites, but it also helps with social bonding.
Conclusion
So, there you have it – five key diagrams simplifying the anatomy of a cat.
By breaking down the external features, skeletal structure, muscular system, respiratory system, digestive system, circulatory system, nervous system, and reproductive system, you now have a better understanding of how all these components work together to make up a cat's anatomy.
Keep exploring and learning more about these fascinating creatures!