4 Best Resources for Basic Cat Anatomy and Physiology
Did you know that domestic cats have a total of 244 bones in their bodies?
Curious about the intricate details that make up your feline friend's anatomy and physiology?
From the digestive system to the circulatory system, there are four key resources that can provide you with a solid foundation for understanding your cat's inner workings.
Whether you're a new cat owner or simply interested in learning more about your pet, these resources will help you grasp the complexities of cat anatomy and physiology.
Understanding Cat Digestive System
If you're curious about how a cat's digestive system works, this subtopic will provide you with a clear overview. Cats have a unique digestive process that's designed to efficiently break down food and extract nutrients for their well-being. The journey starts in the mouth, where cats use their sharp teeth to chew food before swallowing. Once swallowed, the food travels down the esophagus into the stomach, where powerful acids and enzymes begin the breakdown process.
From the stomach, the partially digested food moves into the small intestine, where most of the nutrient absorption takes place. The small intestine is lined with villi, tiny hair-like structures that increase the surface area for nutrient absorption. Here, nutrients such as proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals are absorbed into the bloodstream to be utilized by the cat's body for energy and growth.
After the small intestine has absorbed the majority of the nutrients, the remaining waste moves into the large intestine, where water is reabsorbed to form feces. Finally, the waste is expelled through the rectum and out of the body. Understanding the cat's digestive process and nutrient absorption is crucial for ensuring they receive the necessary nutrients to thrive and stay healthy.
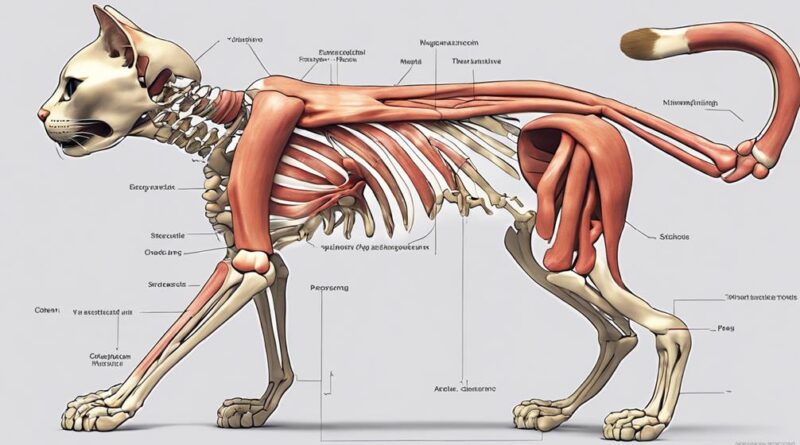
Exploring Feline Musculoskeletal Structure
To understand the intricate feline musculoskeletal structure, it's essential to grasp how the cat's skeletal system supports its overall anatomy and movement. Cats have a remarkable musculoskeletal system that enables them to exhibit agility, grace, and strength in their movements. Here are some key aspects to consider when exploring the feline musculoskeletal structure:
- Joint Flexibility: Cats possess a wide range of motion in their joints, allowing them to leap, climb, and stretch with ease. Their flexible joints contribute to their incredible agility and acrobatic abilities.
- Muscle Strength: The feline musculature is well-developed and powerful, providing cats with the strength needed for activities like hunting, running, and climbing. Strong muscles support their movements and help them navigate various terrains effortlessly.
- Skeletal Support: The cat's skeleton serves as the framework that supports its body and provides structure for the muscles to attach to. The skeletal system plays a crucial role in maintaining the cat's posture and overall body shape.
- Locomotion Efficiency: The coordination between the cat's muscles, bones, and joints ensures efficient locomotion. Cats are known for their graceful movements and swift reflexes, which are facilitated by their well-adapted musculoskeletal system.
Understanding these aspects of feline musculoskeletal structure can provide valuable insights into how cats move, interact with their environment, and exhibit their natural behaviors.
Diving Into Cat Respiratory System
Delving into the cat's respiratory system reveals a complex network of organs and structures crucial for their breathing and overall health. The respiratory system functions in cats, much like in humans, to ensure the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide necessary for cellular function. Cats breathe through their nostrils, with the air then passing through the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and finally into the lungs. Within the lungs, tiny air sacs called alveoli facilitate the gas exchange process, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled.
Understanding the respiratory system in cats is essential for recognizing signs of feline respiratory disorders. Common respiratory issues in cats include infections like feline viral rhinotracheitis, feline calicivirus, and feline infectious peritonitis. These infections can lead to symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, nasal discharge, and difficulty breathing. Other respiratory disorders in cats may include asthma, pneumonia, and bronchitis. Prompt veterinary attention is crucial if you notice any abnormalities in your cat's breathing or respiratory patterns.
Cat's Circulatory System Essentials
Exploring the essential components of a cat's circulatory system reveals a network of vessels and organs vital for maintaining feline health and well-being.
- Efficient Blood Flow: Cats have a complex circulatory system that ensures the delivery of oxygen and nutrients throughout their bodies.
- Heart Function: The feline heart plays a crucial role in pumping blood to all parts of the body, ensuring proper circulation.
- Vascular Network: Cats have an intricate network of blood vessels that help in the distribution of essential substances and the removal of waste products.
- Regulation of Blood Pressure: The circulatory system in cats helps regulate blood pressure to ensure optimal functioning of vital organs.
Understanding how blood flows through a cat's body and how the heart functions is essential in comprehending their overall health.
The blood flow in cats is responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing waste products like carbon dioxide.
The heart, as the central organ in this system, contracts and relaxes rhythmically to pump blood efficiently.
The interconnected vessels play a crucial role in maintaining feline health by facilitating the circulation process.
Additionally, the regulation of blood pressure ensures that different body systems receive adequate blood supply for optimal functioning.
Cat's Nervous System Basics
After understanding the essential components of a cat's circulatory system, it's crucial to now explore the basics of the cat's nervous system. The nervous system is a complex network responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body, allowing for various functions. At the core of this system is the brain, which plays a vital role in regulating body activities and behaviors. Understanding brain function is key to comprehending how your cat interacts with its environment and processes information.
Neuron communication is another fundamental aspect of the cat's nervous system. Neurons are specialized cells that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals. These signals travel along the neuron's axon to reach other neurons or target cells, enabling communication within the body. In cats, neuron communication is essential for basic functions like movement, sensory perception, and cognitive processes.
The brain coordinates these neuron communications, processing sensory inputs, initiating responses, and storing memories. This intricate network of neurons and brain function allows your cat to exhibit behaviors, learn from experiences, and adapt to different situations. By understanding the basics of the cat's nervous system, you can gain insight into your feline companion's behaviors and overall well-being.
Cat's Reproductive Anatomy Overview
The cat's reproductive anatomy comprises specialized structures essential for breeding and reproduction. When it comes to understanding the reproductive anatomy of cats, there are key points to consider:
- Female Cat Anatomy: The female cat has a reproductive system that includes ovaries, oviducts, a uterus, cervix, and vagina. These structures play vital roles in the cat's ability to conceive and carry offspring.
- Male Cat Reproductive Organs: Male cats have testes responsible for producing sperm, which is then transported through the vas deferens and combines with fluids from accessory glands to form semen. The penis is essential for delivering the semen into the female reproductive tract during mating.
- Reproductive Hormones: Both male and female cats have specific hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone in females, and testosterone in males, that regulate the reproductive cycle and behavior.
- Mating Behaviors: Cats exhibit unique mating behaviors influenced by their reproductive anatomy and hormonal changes. Understanding these behaviors is crucial for breeders and pet owners alike.
Cat's Skin and Coat Structure

Cat's skin and coat structure play crucial roles in not just their appearance but also their overall health and well-being. The skin is the largest organ of a cat's body, providing protection against external factors and regulating body temperature. Underneath the skin, you'll find a complex network of blood vessels, nerves, and glands that contribute to the skin's structure and function.
When it comes to hair growth, cats have three types of hair: the undercoat, guard hairs, and awn hairs. The undercoat provides insulation, while the longer guard hairs protect against moisture and foreign particles. Awn hairs are shorter and help with sensory functions. Cats shed their fur as a way to regulate body temperature, especially during seasonal changes.
Understanding your cat's skin and coat structure is essential for maintaining their health. Regular grooming not only keeps their coat shiny and free of tangles but also helps distribute natural oils produced by the skin. These oils play a vital role in keeping the skin moisturized and healthy. Additionally, paying attention to any changes in your cat's skin, such as dryness, redness, or lumps, can help you identify potential health issues early on. By taking good care of your cat's skin and coat, you contribute to their overall well-being and happiness.
Cat's Senses and Sensory Organs
Understanding how felines perceive the world around them through their senses and sensory organs is essential for providing optimal care and enrichment for your furry companion. Cats have remarkable sensory capabilities that shape their interactions with their environment. Here are some fascinating insights into your cat's senses and sensory organs:
- Hearing & Vision: Cats have excellent hearing, being able to detect a wide range of frequencies, including ultrasonic sounds. Their vision is designed for hunting, with a keen ability to see in dim light and detect movement effectively.
- Taste & Smell: A cat's sense of taste is less developed compared to humans, with a preference for proteins and fats. However, their sense of smell is incredibly sensitive, allowing them to distinguish various scents and locate food or mark territory.
Cats rely heavily on their senses to navigate the world, communicate, and hunt. Understanding how your cat's senses function can help you create a stimulating environment that caters to their natural instincts. Providing opportunities for sensory enrichment, such as interactive toys, puzzle feeders, and safe outdoor experiences, can enhance your cat's well-being and overall quality of life. By recognizing and respecting your cat's sensory abilities, you can strengthen the bond you share and ensure a fulfilling companionship.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Cats Be Affected by the Same Respiratory Illnesses as Humans?
Yes, cats can be affected by respiratory illnesses similar to humans. Feline allergies can cause issues with their respiratory health. Cat flu, a common viral infection, can impact their immune system and lead to symptoms like sneezing and coughing.
It's essential to monitor your cat's respiratory health and consult a vet if you notice any concerning symptoms to ensure they receive proper care and treatment.
How Does a Cat's Circulatory System Differ From a Human's?
In a cat's circulatory system, there are some key differences compared to a human's. The blood flow variances are notable, with cats having faster heart rates and smaller blood volumes relative to their body size.
Cats also have a higher red blood cell count and more efficient oxygen-carrying capacity. Understanding these distinctions can provide insight into how a cat's body functions uniquely compared to a human's circulatory system.
Do Cats Have a Unique Sense of Taste Compared to Other Animals?
When it comes to feline preferences, cats have a unique sense of taste compared to other animals. Their taste buds play a vital role in their sensory perception and flavor detection.
Cats are known to be more sensitive to bitter tastes than dogs but tend to enjoy meaty and savory flavors. This heightened sense of taste helps cats choose the foods that meet their nutritional needs and satisfy their palates.
What Role Do Hormones Play in a Cat's Reproductive System?
Hormones are vital for your cat's reproductive system. They control the reproductive cycles and ensure everything functions smoothly.
Hormonal regulation plays a key role in heat cycles, mating behavior, and pregnancy. These chemical messengers orchestrate the release of eggs, readiness for mating, and support the development of embryos.
Understanding how hormones impact your cat's reproductive health is crucial for proper care and breeding management.
How Does a Cat's Skin and Coat Structure Help Regulate Their Body Temperature?
Your cat's skin and coat structure play a crucial role in regulating their body temperature. Thermoregulation mechanisms, such as sweat glands and blood vessels in the skin, help dissipate heat.
Additionally, the hair structure adaptations, like insulating undercoats and guard hairs, aid in trapping air for warmth or cooling. This combination of skin and coat features allows your feline friend to maintain a stable body temperature regardless of external conditions.
Conclusion
So, now you have a good grasp on the basic anatomy and physiology of cats.
Remember to keep learning and exploring more about your feline friend's health and well-being.
Understanding these key aspects will help you better care for your cat and ensure they live a happy and healthy life.
Keep observing, researching, and staying informed to provide the best care possible for your beloved pet.